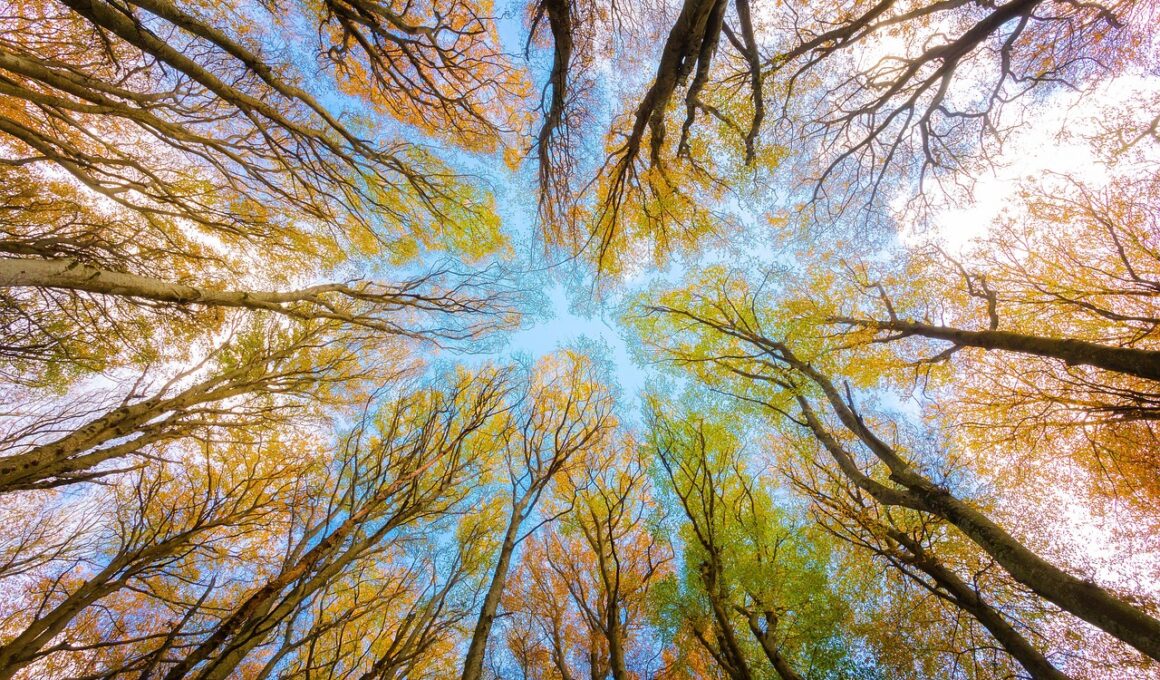
The Role of Forest Canopies in Regulating Fitness-Enabling Microclimates
Forest canopies play a critical role in providing microclimates that enhance environmental fitness for numerous species. Through their ability to absorb sunlight, reduce wind speeds, and retain moisture, canopies create ideal living conditions for flora and fauna. In terrestrial ecosystems, these upper layers of trees shield understory plants and animals from extreme weather changes, enhancing the biodiversity beneath them. Canopy temperatures can be significantly cooler than ground levels, creating a supportive habitat. This phenomenon is essential for maintaining a resilient ecological balance, offering protection and nourishment to young plants and small creatures. Furthermore, canopies help mitigate the intensity of solar radiation reaching the forest floor, which significantly affects soil moisture levels. By controlling temperature and humidity, forest canopies contribute to greater atmospheric stability, fostering a consistent growth pattern in various species. The importance of forest management in maintaining healthy canopies cannot be understated. Sustainable practices ensure that we safeguard these vital ecosystems. Preservation of existing forests and restoration of damaged areas can lead to improved microclimate conditions that ultimately allow a wider range of species to thrive.
The canopy’s role extends beyond mere shelter, influencing local climate, nutrient cycling, and overall forest health. The foliage intercepts rainfall, reducing soil erosion, and promoting water infiltration, which benefits plant roots below. This process aids in nutrient transition throughout the ecosystem, ensuring that essential minerals circulate efficiently. As leaves fall and decompose in the canopy, they contribute organic matter back to the soil. This enriches the ground layer, fostering a thriving community of microorganisms essential for breaking down organic matter. Consequently, healthier soils yield more diverse and resilient plant life. Forest canopies also support complex food webs. Birds, insects, and mammals all depend on this layer for sustenance, relying on insects, fruits, or seeds found within. Protecting this critical habitat is necessary for preserving these intricate relationships that define forest ecosystems. With climate changes putting additional stress on forests, it is vital to adopt adaptive management strategies. Innovative policies and practices designed to conserve and enhance forest canopies can help combat challenges posed by climate change. Collaboration between stakeholders, including governments and local communities, can ensure these ecosystems are better protected against future threats.
Enhancing Biodiversity Through Canopy Protection
One of the most compelling aspects of forest canopies is their influence on biodiversity. The structural complexity of these upper layers creates microhabitats that are home to countless species. Mosses, ferns, epiphytes, and numerous insects flourish, significantly contributing to overall ecosystem diversity. The variety of plants that grow in the canopy supports numerous animal species, creating a rich tapestry of life. This diversity boosts ecological resilience, helping forests withstand environmental changes and disturbances, such as pests or disease outbreaks. Effective forest management practices can help enhance biodiversity by protecting existing canopy structures. Creating buffer zones around critical habitats, promoting selective logging, and restoring degraded areas can lead to healthier forest ecosystems. It’s essential to recognize the interconnectedness of life within these canopies. For instance, pollinators that thrive in canopy conditions significantly contribute to plant reproduction, leading to an even greater diversity in plant species. Communities that rely on forest resources should be educated about the importance of preserving these habitats. Promoting sustainable practices, such as reforestation and eco-tourism, can provide community benefits while safeguarding biodiversity.
Another vital function of forest canopies is their contribution to carbon sequestration. The trees within the canopy absorb carbon dioxide, a significant greenhouse gas, thereby playing a crucial role in mitigating climate change. As trees grow, they sequester carbon in their biomass and in the surrounding soil, resulting in lower atmospheric carbon levels. Forest management techniques that promote healthy growth dynamics can maximize this carbon sink. Practices like thinning overcrowded stands can enhance growth rates, enabling trees to capture even more carbon as they mature. Furthermore, maintaining diverse tree species is essential for long-term carbon storage. Different species have unique growth rates and carbon capture abilities, contributing to a more effective overall carbon sequestration strategy. In addition to carbon capture, forest canopies are crucial in regulating local weather patterns. They can influence rainfall distribution, temperature variations, and humidity levels that are essential for maintaining adjacent ecosystems. Climate models are increasingly recognizing the role of forest canopies in broader climate regulation. Investing in the protection of these canopies is a fundamental part of climate strategies that aim for reductions in greenhouse gas emissions on a global scale.
The Importance of Community Engagement in Forest Conservation
Community engagement is vital for effective forest management and conservation efforts designed to protect forest canopies. Local communities, often bearing the consequences of deforestation or degradation, have a profound understanding of their surrounding environments. Empowering them through education and involvement can lead to sustainable practices that protect essential canopy layers. Programs that promote sustainable forestry, agroforestry, and responsible land use can significantly reduce the pressure on forest ecosystems. Knowledge-sharing platforms can facilitate the exchange of experiences and strategies among various stakeholders, including conservationists, policy-makers, and residents. By incorporating local knowledge into forest management plans, we can develop practices that align with the ecological realities and cultural values of the communities. This collaboration can lead to more effective interventions in preserving forest canopy health. Additionally, engaging communities in monitoring canopy health can foster a sense of ownership over natural resources. When people are invested in the protection of their local forests, they are more likely to uphold regulations and support conservation initiatives. Ultimately, a united approach combining scientific knowledge and indigenous practices can yield better outcomes for our forests.
Moreover, innovative technologies are emerging as powerful tools for monitoring and managing forest canopies. Remote sensing technologies, such as satellite imagery and drones, have revolutionized our capability to assess forest health and changes efficiently. These tools allow for the collection of high-resolution data on canopy cover, tree health, and species diversity. By analyzing this information, forest managers can make informed decisions regarding conservation strategies and resource allocation. Furthermore, machine learning can identify trends over time, helping to predict future environmental changes and inform proactive management initiatives. Despite these advancements, community involvement remains essential in integrating technology with traditional methods. Eliciting local input regarding the application of these technologies can enhance their effectiveness. Communities can provide valuable insight into ground-level conditions that satellite data may overlook. By combining local knowledge with technology-driven approaches, we can develop comprehensive strategies for forest management that protect both biodiversity and microclimate stability. This holistic view recognizes that healthy forest canopies are crucial for preserving environmental fitness at multiple levels, ensuring the continuity of diverse ecosystems.
Conclusion: Sustainable Forest Management for Future Generations
In conclusion, sustainable forest management that focuses on preserving forest canopies is essential for regulating fitness-enabling microclimates. These upper layers of trees provide numerous ecological benefits, including biodiversity support, soil health, and climate moderation. Adopting practices that promote canopy integrity will lead to a more balanced ecosystem while creating a stable environment for various flora and fauna. Importantly, engaging local communities in conservation efforts ensures that diverse knowledge systems inform management strategies. Additionally, incorporating advanced technology can enhance the effectiveness of these initiatives, leading to improved monitoring and management outcomes. By fostering collaborative partnerships among stakeholders, we can develop holistic strategies that protect and enhance forest canopies. Future generations will rely on the health of these ecosystems for their well-being. Therefore, it is imperative that we act now to ensure the preservation of our forests. This proactive approach will not only support biodiversity but will also work substantially towards combating climate change. Investing in forest management today is an investment in a healthier planet for tomorrow.
Forests are essential to human survival and the well-being of our planet, representing a critical component in sustainability initiatives globally. Their intricate ecosystems regulate essential environmental processes while offering numerous resources and aesthetic values. Forest management practices aimed at enhancing canopy health will ensure these benefits persist into the future for our communities and the ecosystems they encompass. Thus, a sustainable relationship with our forests can establish a pathway to a balanced coexistence that significantly improves overall environmental fitness.