Exercise Guidelines for Older Adults with Chronic Diseases
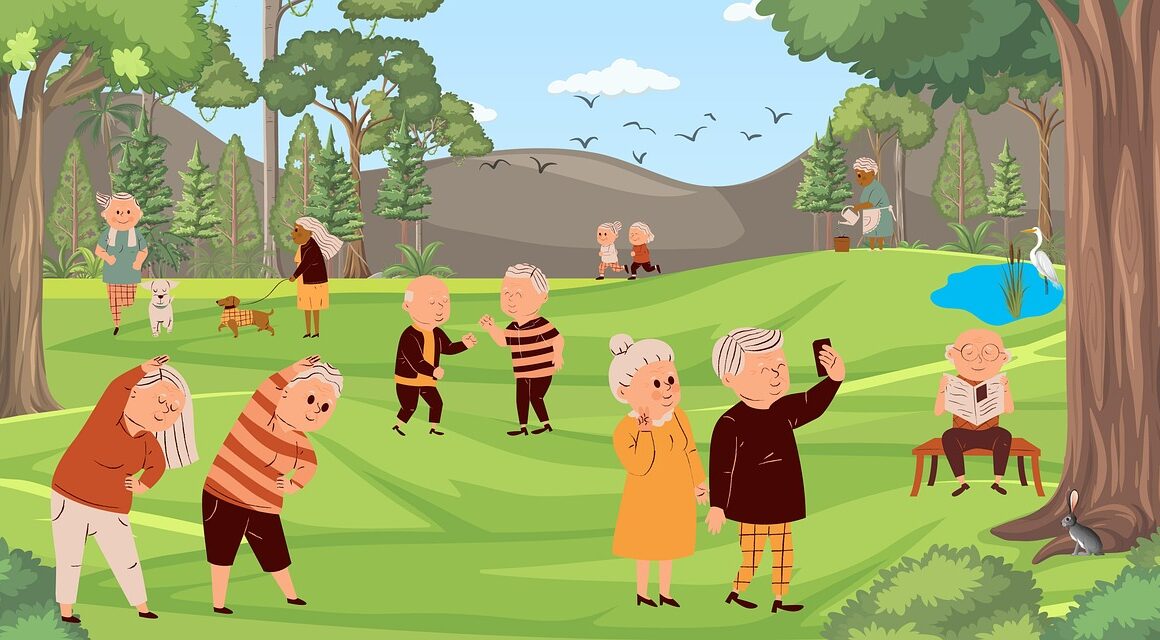
Older adults facing chronic diseases are encouraged to integrate exercise as part of their health management strategy. Exercise can effectively enhance functional abilities and improve overall health. A well-structured program should consist of at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activities each week. This can include walking, cycling, or swimming at a pace that allows conversation yet raises the heart rate. Strength training should also be a part of the routine, performed two or more days each week targeting all major muscle groups. Flexibility and balance exercises are equally essential, reducing the risk of falls and promoting independence. The key is personalization; each individual’s exercise program should be tailored to their medical conditions, abilities, and preferences. Prior to starting any exercise regimen, it is crucial for older adults to consult healthcare professionals to assess their fitness level and any specific limitations. Engaging in community-based exercise programs can also provide support and motivation. Remember, consistency is vital in maintaining the benefits of exercise, both physically and mentally. This way, older adults can significantly improve their quality of life and manage chronic conditions effectively.
Recognizing the importance of safety is fundamental when older adults with chronic diseases engage in exercise. It is essential to listen to one’s body and modify activities as needed. A proper warm-up and cool-down can prevent injuries and aid in recovery. Start slowly and gradually increase intensity to avoid undue stress on the body. A heart rate monitor can help track intensity to ensure one stays within a safe range while exercising. Individuals should also stay hydrated during physical activity, as dehydration can lead to additional complications, especially in older adults. It’s advisable to wear appropriate footwear and clothing that allows for movement and support. Activities should be enjoyable; finding a workout buddy or group can enhance motivation and make the sessions more enjoyable. Low-impact classes such as chair yoga, tai chi, or water aerobics are excellent choices for older adults. Establishing clear, achievable goals can also provide a sense of direction and accomplishment. Record progress to stay engaged and motivated throughout the journey. Remember to evaluate and adapt exercise routines regularly to suit changing health conditions or personal fitness levels.
Types of Exercises Suitable for Older Adults
A well-rounded exercise program for older adults should include three primary types of activities: aerobic, strength, and flexibility exercises. Aerobic exercises, such as brisk walking, swimming, and cycling, elevate heart rates and enhance cardiovascular health while improving endurance. These activities are typically low-impact yet effective in maintaining overall fitness levels. Strength exercises, using resistance bands or light weights, play a crucial role in combating age-related muscle loss. Establishing strong muscles is vital for maintaining functional independence and reducing injury risk. Flexibility exercises, such as stretching or yoga, are essential for maintaining joint health and ease of movement. Incorporating these elements into routines will optimize health benefits. Additionally, balancing exercises such as standing on one foot or using balance boards help reduce fall risk. Engaging in activities that promote both mental and physical health, such as games that involve movement or social engagement, can be also beneficial. Ultimately, a personalized mix ensures that older adults remain active while making significant strides toward improving their health and well-being.
Community resources and support systems play a vital role in encouraging older adults to stay committed to their exercise routines. Engaging in local fitness programs or group exercises can foster a sense of belonging and motivation. These environments often provide social interaction, enhancing mental well-being alongside physical activity. Many community centers offer specialized programs catering specifically to older adults; these include low-impact aerobics, gentle yoga, and circuit training that focus on strength, flexibility, and balance. Virtual classes have also gained popularity, enabling accessibility for those unable to travel. Support from family and friends can help motivate individuals to stay active and maintain long-term exercise habits. It is beneficial to educate family members about the importance of physical activity for older adults, fostering a supportive atmosphere. Encouraging partnerships in fitness activities enhances accountability and makes workouts more enjoyable. Participating in social events that include movement, like dance or group walks, can also contribute significantly to overall health. As older adults explore options within their community, they can create a sustainable approach to fitness that aligns with their lifestyle and goals.
Overcoming Barriers to Exercise
Despite the tremendous benefits of exercise, many older adults face barriers that prevent them from maintaining an active lifestyle. Common obstacles may include physical limitations, chronic pain, lack of motivation, or fear of injury. Addressing these challenges requires a proactive approach. Collaborating with healthcare providers can lead to tailored fitness programs that consider individual health conditions and restrictions. Implementing pain management strategies may also help alleviate concerns surrounding exercise. Additionally, the role of motivation cannot be understated; setting short-term goals, joining exercise groups, or seeking a workout partner can significantly foster adherence to routines. Resources such as exercise classes specifically aimed at seniors can provide encouragement and enjoyment through social engagement. Educating seniors about the risks versus rewards of inactivity can encourage them to prioritize their health. Techniques such as visualization and positive self-talk can also empower older adults to commit to exercise. Lastly, tracking progress through daily logs or apps can provide visible evidence of improvement, reinforcing the commitment to stay active and healthy in the long term.
Nutrition plays a crucial role in conjunction with exercise for older adults managing chronic diseases. A balanced diet helps support overall health and optimizes the benefits of physical activity. Including a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats is essential in daily meal plans. Proper nutrition assists in muscle growth, recovery, and energy levels. Staying adequately hydrated cannot be overlooked; encouraging older adults to drink water before, during, and after exercise promotes functionality and decreases the risk of dehydration-related health issues. Supplements can be beneficial, especially if nutritional deficiencies are identified; however, these should be taken under medical guidance. Planning meals to align with exercise activities can also provide fuel needed for energy during workouts. Encouraging family involvement in meal preparation can promote healthier eating habits as well. Lastly, being mindful of portion sizes can prevent over or under-eating, ensuring that nutritional needs are sufficiently met without compromising health goals. As older adults gain knowledge about nutrition, they empower themselves to maximize their exercise efforts and improve their health trajectories effectively.
Final Thoughts on Exercise and Chronic Diseases
In conclusion, incorporating exercise into the daily routines of older adults with chronic diseases is essential for improving overall health and quality of life. While challenges may arise, the numerous benefits of staying active far outweigh the obstacles. Developing personalized exercise plans that focus on aerobic, strength, flexibility, and balance workouts ensures comprehensive physical fitness. Engaging with community resources and support systems facilitates not only adherence but fosters a sense of belonging among peers. Nutrition, combined with appropriate physical activity, enhances effectiveness in managing chronic diseases. As older adults prioritize both exercise and healthy eating, they experience substantial improvements in their well-being. Solutions to barriers often lie in understanding individual needs; collaboration with healthcare providers can provide the necessary guidance to navigate challenges effectively. The journey toward a more active and fulfilling lifestyle is possible with commitment, education, and support. Encourage older adults to embrace change and view physical activity as an indispensable aspect of maintaining health. Together, we can work towards empowering seniors to achieve their fitness and health goals, enabling them to lead healthy, active lives well into their golden years.
Overall, it is essential for healthcare professionals, caregivers, and family members to recognize the importance of exercise in managing chronic conditions among older adults. We should actively encourage and facilitate their participation in physical activities. Focused efforts should be made to educate older adults on the benefits and safety of exercise. Providing accessible resources, such as exercise classes tailored to their abilities, can also make a significant difference. Supporting their endeavors through motivation and companionship is vital for long-term adherence. Each step taken towards physical improvement should be celebrated, fostering a positive attitude toward exercise. Engaging with local health organizations or community programs can provide additional opportunities to participate in regular physical activity effectively. Adapting environments to be elder-friendly fosters participation and can positively impact their well-being. Ultimately, collective efforts in promoting exercise among older adults managing chronic diseases will lead to healthier, more fulfilling lives. As we work together in enhancing their quality of life, we empower them to take charge of their health journey, navigate challenges, and experience the countless rewards that come from remaining active.