Intermittent Fasting and Its Role in Alleviating Digestive Issues
Intermittent fasting (IF) has gained popularity due to its potential health benefits, especially concerning gut health. By alternating periods of eating and fasting, the body can recalibrate its digestive processes. Proponents argue that fasting periods lead to improved digestion, less bloating, and enhanced nutrient absorption. Research suggests that IF may positively influence the gut microbiome, the community of microorganisms residing in the digestive tract. A balanced microbiome supports optimal digestive function and can alleviate various gastrointestinal concerns. Moreover, studies indicate that intermittent fasting can help reduce inflammation, leading to a calmer digestive system. This makes IF an attractive option for individuals prone to digestive discomfort. By reducing overall food intake, the digestive system is less burdened, allowing for adequate time to process and repair itself. In fact, some research correlates IF with the promotion of beneficial gut bacteria while decreasing harmful ones. This shift in microbial balance not only enhances digestion but can also improve overall health. Thus, as understanding deepens regarding IF’s impact on gut health grows, many are exploring this dietary approach as a solution for digestive issues. Individuals are encouraged to consult healthcare professionals before starting anyone fasting regimen.
The effects of intermittent fasting on digestion extend beyond mere convenience and time management. When the body undergoes fasting, it initiates autophagy, a crucial cellular process where cells eliminate waste and repair themselves. This mechanism can significantly impact gut health, as it functions to cleanse and rejuvenate intestinal cells. During fasting, the digestive system gets a much-needed break, allowing for proper repair and maintenance of physiological functions. Notably, intermittent fasting can also influence gastric acid secretion and digestive enzyme activity, promoting optimal digestion efficiency. A marked decrease in chronic inflammation may follow, further helping those with gastrointestinal disorders to find relief. Furthermore, intermittent fasting is said to correlate positively with an improved sense of satiety and appetite control. Consequently, this can lead to healthier food choices when not fasting. Understanding the right approach and timing when adopting intermittent fasting is crucial. Individuals can consider methods such as the 16/8 approach, which involves fasting for 16 hours and restricting eating to an 8-hour window. This can simplify meal planning while providing the gut ample time to perform necessary functions and reset itself.
The Microbiome Connection
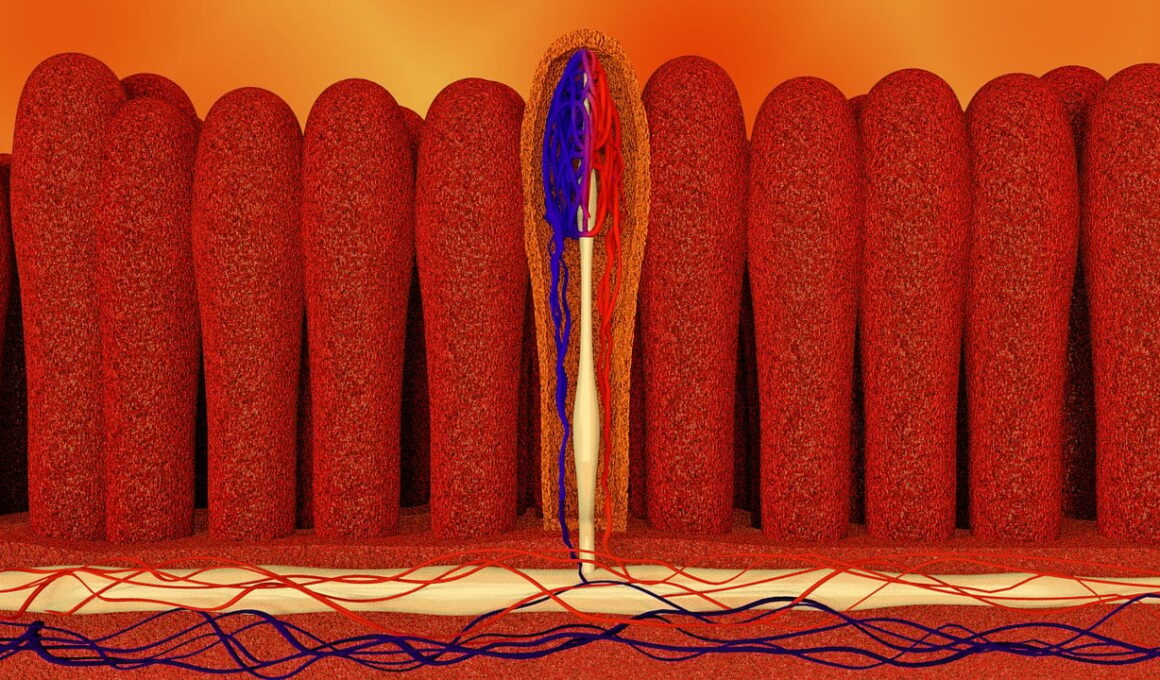
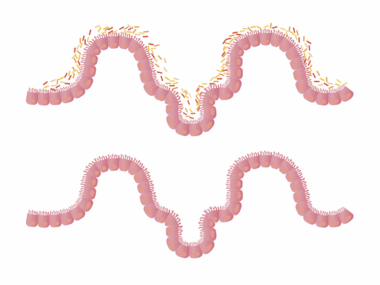
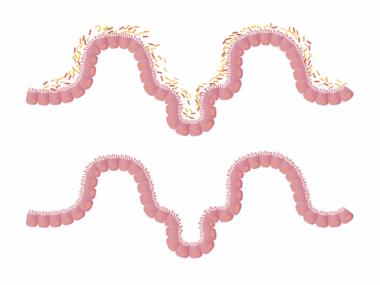
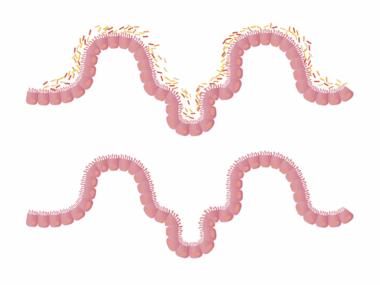
The gut microbiome encompasses trillions of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. A healthy microbiome is essential for digesting food, synthesizing vitamins, and protecting against pathogens. Intermittent fasting has been shown to support a diverse microbiome by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria. Studies indicate that fasting conditions create an environment conducive to favorable gut bacteria proliferation while minimizing the growth of harmful strains. Additionally, improved gut permeability achieved through IF can enhance nutrient absorption, which is crucial for overall wellness. The interaction between diet, lifestyle, and gut health cannot be overstated. When individuals switch to an intermittent fasting lifestyle, they often incorporate healthier food choices during eating windows, fortifying their microbiome with prebiotics and probiotics. This practice contributes to a balanced environment in the gut, which significantly influences metabolic processes and immune function. Implementing sufficient hydration during fasting periods further fosters gut health by preventing dehydration and supporting digestion. In summary, adopting intermittent fasting practices alongside a balanced diet can create a microbiome that supports digestive health and overall physiological well-being.
Implementing intermittent fasting does not require drastic lifestyle changes but rather strategic adjustments to one’s daily routine. For those struggling with digestive disorders, this approach can be transformative. Establishing a fasting schedule personalized to individual needs promotes adherence and ensures long-term success. When starting, it’s essential to listen to your body. The initial phase may involve minor discomfort as the body adjusts. However, many individuals report a swift decrease in digestive issues, such as bloating and gas. Remote influencers and testimonials increasingly spotlight these positive effects, inspiring others to give IF a try. Alongside fasting, maintaining a diet rich in fibrous foods, lean proteins, and good fats can amplify benefits. Foods high in fiber aid digestion, prevent constipation, and provide the nutrients needed for a healthy microbiome. The emphasis on whole, nutrient-dense foods is vital during eating windows to maximize metabolic health. Consistency and patience are crucial, providing the body ample opportunity to adjust. As individuals engage with this lifestyle, the profound effects of intermittent fasting on gut health can inspire deeper inquiry into nutritional choices and their impacts on overall health.
Potential Challenges and Considerations
While intermittent fasting showcases potential benefits, it may not be a one-size-fits-all solution and could pose challenges for some individuals. It’s vital to monitor personal responses when adopting a fasting regimen, as everyone’s body reacts differently. Some may experience heightened hunger or irritability, especially in the initial phases, which can deter motivation. For those with existing health conditions or who are pregnant, it’s essential to seek professional guidance prior to commencement. This ensures any potential adverse effects on health are minimized. Furthermore, another consideration involves meal quality during eating windows. Relying on nutrient-poor, processed foods can negate fasting benefits and lead to issues such as nutrient deficiencies. The balance of food quality remains paramount for achieving optimal health outcomes while practicing intermittent fasting. Gradually establishing eating windows, staying attuned to body signals, and selecting high-quality foods can facilitate a smoother transition into fasting. As more people explore this lifestyle, experimental findings regarding interpersonal variability continue to emerge, reinforcing the necessity of personalized approaches to dietary strategies.
Incorporating intermittent fasting into a lifestyle may also evoke a sense of community among practitioners. Social support can play a significant role in enhancing the fasting experience, prompting individuals to share their journeys, challenges, and successes. Various online communities and social media platforms foster communications among those practicing intermittent fasting, encouraging knowledge sharing related to gut health. Many individuals document their progress through blogs, vlogs, and social media, highlighting the transformative potential of IF for digestive issues and overall health. This exchange of experiences can serve as a motivational tool for others considering intermittent fasting. In addition to community support, participation in workshops and information sessions can augment understanding regarding the relationship between fasting and gut health. Engaging with experts adds credibility to personal experiences and may assist in navigating individual challenges encountered. This collective approach not only fosters enthusiasm for intermittent fasting but can also celebrate successes that highlight personal growth in health and wellbeing. Moreover, tapping into shared resources can enrich the fasting journey, allowing for more informed choices regarding nutrition and lifestyle alterations.
Final Thoughts and Recommendations
As the exploration of intermittent fasting continues, its connection to gut health reveals promising avenues for enhancing digestive wellness. Integrating IF into daily life can offer a wide array of benefits, from improved digestion to a more robust microbiome that supports overall health. However, individual experiences may vary, emphasizing the importance of personalized approaches. When embarking on this journey, attention to nutrient quality, hydration, and dietary balance remains paramount. Listening to your body and adjusting fasting protocols as necessary can yield valuable insights into personal health patterns. Before committing, consider researching available resources and expert recommendations, which can underscore the importance of proper implementation. Ultimately, the integration of intermittent fasting should align with one’s lifestyle preferences and wellness goals, making it a sustainable practice. Whether you’re experiencing digestive issues or seeking overall health improvement, intermittent fasting may be a beneficial strategy. As you explore this approach, celebrate each small victory while staying mindful of your body’s responses. Embracing this holistic dimension of health can lead to lasting improvements, encouraging ongoing curiosity about food and fasting’s profound influence on our gut and wellness.
In summary, intermittent fasting serves as a viable option for individuals looking to enhance their gut health through strategic alterations in their eating habits. As research evolves and awareness grows, the benefits of this dietary practice become increasingly apparent. The potential for fasting to alleviate digestive issues is underscored by its impacts on the microbiome and overall digestive function. When pursued with mindful intent and informed choices, intermittent fasting can foster a more favorable environment for gut health. As with any health journey, knowledge, community engagement, and resilience are central to achieving success. Therefore, individuals are encouraged to educate themselves thoroughly while remaining open to adjusting their strategies based on personal experiences. When embarking on a path toward better digestive health, consider intermittent fasting as a component of your overall health strategy. By maximizing the benefits of this dietary approach, individuals can not only find relief from digestive concerns but also cultivate a deeper understanding of their nutritional needs. The interplay between food, fasting, and gut health is complex, yet rewarding. Embrace this journey toward improved wellbeing and discover the potential benefits of a harmonious, mindful dietary lifestyle.