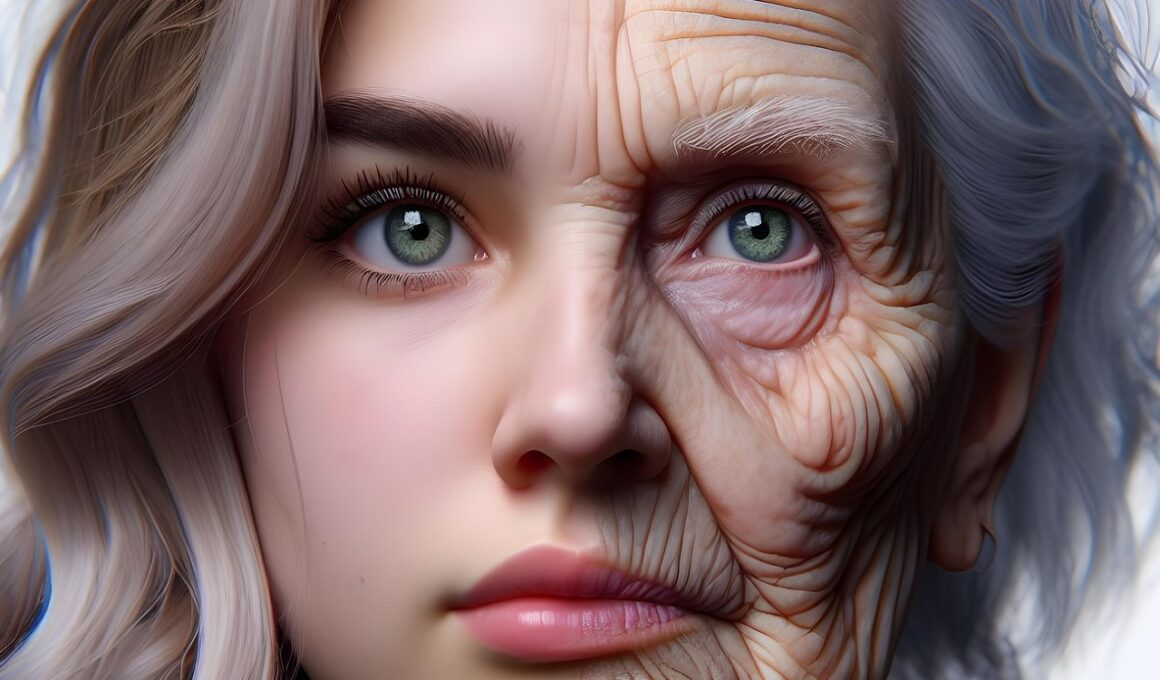
The Relationship Between Body Water and Aging
Body water is essential to life and plays a crucial role in overall health. As we age, our body composition naturally changes, notably impacting the water content in our bodies. Research indicates that adults typically have about 60% body water, but this percentage decreases with age. This reduction can lead to various health complications, such as dehydration and impaired physiological function. Understanding these changes is vital, as hydration is linked to numerous bodily functions, including temperature regulation, nutrient transport, and waste elimination. In older adults, these functions become even more important because they often experience diminished thirst sensation and lower fluid intake voluntarily. Maintaining proper hydration is critical for supporting metabolic processes and skin elasticity. Furthermore, lower body water can affect muscular strength and endurance, impacting the ability to engage in physical activities. As hydration status influences cognitive performance, not drinking enough water can lead to decreased mental clarity and focus. Adequate hydration may also mitigate the risk of chronic diseases, including kidney stones and urinary tract infections. Therefore, understanding the correlation between body water and aging is essential for promoting better health outcomes in older individuals.
Body composition changes with age impact many aspects of health, notably body fat and lean mass. The decrease in total body water can result in higher percentages of body fat, which can lead to various health concerns. Higher levels of body fat are often associated with increased risks of cardiovascular diseases and diabetes. Furthermore, an increase in adipose tissue can negatively affect functional mobility, reducing overall quality of life. Understanding how body composition shifts can empower individuals to take charge of their health as they age. It emphasizes the importance of regular physical activity and balanced nutrition. Regular exercise, especially strength training, can help preserve lean muscle mass while minimizing fat gain. Additionally, proper nutrition ensures that the body receives necessary nutrients to maintain hydration levels. Consuming foods with high water content, like fruits and vegetables, can be beneficial. It’s also essential to note that hydration needs can vary based on activity levels, environment, and health conditions. Hence, it’s prudent for older adults to assess their hydration regularly. Educating communities on these aspects can help foster healthy habits, enhancing longevity and quality of life.
The Importance of Hydration
Hydration is integral to maintaining optimal health, especially as one ages. Water serves as a primary component of bodily fluids, influencing numerous metabolic processes, including digestion, circulation, and excretion. The elderly often neglect hydration due to factors like reduced thirst perception, mobility challenges, or medication side effects. Studies illustrate that even mild dehydration can lead to confusion, lethargy, and impaired cognitive function. These symptoms can exacerbate age-related health issues, making it essential to prioritize hydration. In addition to these cognitive impacts, proper hydration contributes to maintaining cardiovascular health. Well-hydrated individuals tend to experience lower blood pressure and improved circulation, thereby enhancing overall heart health. Proper hydration can also boost skin health, reducing signs of aging. Collagen levels in the skin, crucial for its elasticity, remain optimal when adequately hydrated. Furthermore, the kidneys play a significant role in regulating fluid levels, and chronic dehydration can lead to the development of kidney stones or urinary infections. To encourage seniors to drink more water, caregivers and family members can offer water-infused beverages, easily available during meals, and promote the habit throughout the day. Regular check-ins can help maintain proper hydration practices.
Nutrition plays a crucial role in the relationship between body water and aging, necessitating a carefully balanced approach. Foods rich in water content can enhance overall hydration levels and health. Fruits like watermelon, oranges, and strawberries, in addition to vegetables like cucumbers and lettuce, provide both hydration and vital nutrients. Older adults can benefit significantly from incorporating more of these foods into their diets, especially when hydration needs increase. Not only do these foods help maintain hydration, but they are also low in calories, assisting in weight management. Additionally, it is important to consider factors like sodium intake, as excessive sodium can lead to water retention, increasing the risk of hypertension. Replacing processed foods with whole foods can improve hydration and provide antioxidants and vitamins for better health outcomes. Otherwise, sugary beverages should also be limited, as they can lead to further dehydration and unwanted weight gain. Moreover, education surrounding healthy eating habits can significantly impact the well-being of older adults. Encouraging mindfulness when consuming food can boost motivation towards healthier choices and improve overall health, particularly as aging can often lead to a decline in nutritional intake.
Maintaining Healthy Water Levels
Maintaining healthy water levels in the body as we age signifies a proactive approach to wellness. Adequate fluid intake directly influences physical performance, cognitive function, and emotional well-being. Active older adults should pay attention to their hydration, especially when engaging in exercise or any physically demanding activities. Water needs vary among individuals, yet a general recommendation is 8 to 10 cups per day for everyone, with potential adjustments based on individual activity levels. Engaging in regular physical activities is essential, as this may increase the body’s fluid demands. Innovative hydration strategies can include monitoring urine color, with light yellow indicating sufficient hydration, while darker shades may signal a need for more fluids. Furthermore, carrying a water bottle throughout the day can encourage regular sipping. Utilizing technology, such as smartphone apps to remind users to drink water, can also foster positive hydration habits. Ultimately, awareness and adaptation to changing hydration needs are vital. Communities can facilitate workshops and educational programs detailing hydration’s role in aging processes. These initiatives can enhance the overall health and longevity of older adults, ensuring they thrive in their golden years.
The impact of body water on aging is further exemplified through its correlation with physical activity levels. Regular exercise increases the body’s demand for water as fluids are lost through sweat and respiration. Therefore, integrating effective hydration strategies into fitness routines becomes imperative for older adults. Exercise not only enhances functional independence but promotes cardiovascular health, muscle strength, and mental well-being. Additionally, hydration supports muscle recovery post-exercise, combating soreness and fatigue. The elderly should be encouraged to include both aerobic activities and strength-training exercises into their weekly routines while ensuring adequate hydration pre, during, and post-exercise. Hydration should be viewed as a critical element that complements a holistic approach to health and fitness among older adults. Furthermore, individuals can track their physical responses to different hydration levels, contributing to a more personalized understanding of their body’s requirements. Social interactions through group exercises not only keep spirits high but can reinforce hydration habits among peers through supportive encouragement. This communal effort helps eliminate potential barriers that hinder consistent fluid intake. Hence, creating environments that emphasize the importance of hydration can greatly enrich golden years’ quality of life.
Conclusion
In summary, there exists a significant relationship between body water and aging. As individuals age, the physiological changes, including decreased thirst sensation and altered body composition, necessitate a keener focus on hydration. Understanding this relationship can empower older adults to make informed lifestyle choices that positively affect their health. Key strategies include consistent monitoring of fluid intake, prioritizing water-rich foods, and being mindful of daily activities. Such practices can mitigate risks associated with dehydration, particularly as these risks increase with advanced age. Encouraging education about the necessity of adequate hydration can foster proactive health management among older populations. Moreover, implementing community programs can assist in building supportive networks where individuals can share experiences and tips on maintaining hydration. Ultimately, enhancing awareness around the relationship between body water and aging can lead to improved health outcomes, increasing both longevity and quality of life in older adults. Therefore, a comprehensive approach combining education, community support, and individualized hydration strategies is essential in promoting healthier lifestyles among aging populations.
In conclusion, recognizing the critical aspects of hydration concerning body composition highlights the broader implications for aging individuals. As research continues to evolve, ongoing studies can help identify optimal hydration practices and their physiological impacts. Encouraging the elderly to prioritize hydration as part of their daily routine can profoundly influence their overall health. Moreover, supportive social networks and community engagement can also play pivotal roles in reinforcing healthy habits. By fostering environments where hydration is emphasized, we can encourage older adults to engage in discussions about their health, seek assistance, and impart valuable knowledge to one another. These collaborative efforts enhance personal health and create a more informed, health-conscious community. By focusing on hydration as a cornerstone of wellness for aging populations, we can contribute towards a holistic approach to healthy aging. Through education, support systems, and proactive health measures, vitality and longevity can be realized in the golden years. As individuals collectively prioritize these factors, we pave the way for a future where older individuals can thrive, equipped with the necessary tools for optimal well-being. Sustained engagement and education are vital for nurturing healthier aging practices, ultimately leading to enhanced quality of life.