Hormonal Changes Triggered by Gut Dysbiosis
Gut health plays a crucial role in our overall well-being, impacting various aspects of health, including hormonal levels. Gut dysbiosis refers to an imbalance of gut microbiota, which can disrupt hormone production and regulation. This condition can lead to various hormonal changes, affecting energy levels, mood, and metabolic functions. The gut microbiome helps in the digestion of food and the production of certain hormones, such as serotonin and insulin. When this balance is disturbed, hormonal responses can become erratic, leading to potential health issues. It is essential to understand that gut health directly influences hormonal health. For instance, inflammation in the gut can contribute to insulin resistance and increased cortisol levels. These hormonal changes can trigger a cascade of symptoms, including fatigue, weight gain, and digestive issues. Adopting a healthy diet rich in prebiotics and probiotics can support gut health and, consequently, hormone regulation. Foods such as yogurt, kefir, and fiber-rich fruits can promote a healthy gut. Therefore, focusing on gut health is imperative for maintaining hormonal balance in our bodies. Simple dietary changes can significantly impact our hormonal health, emphasizing preventive care.
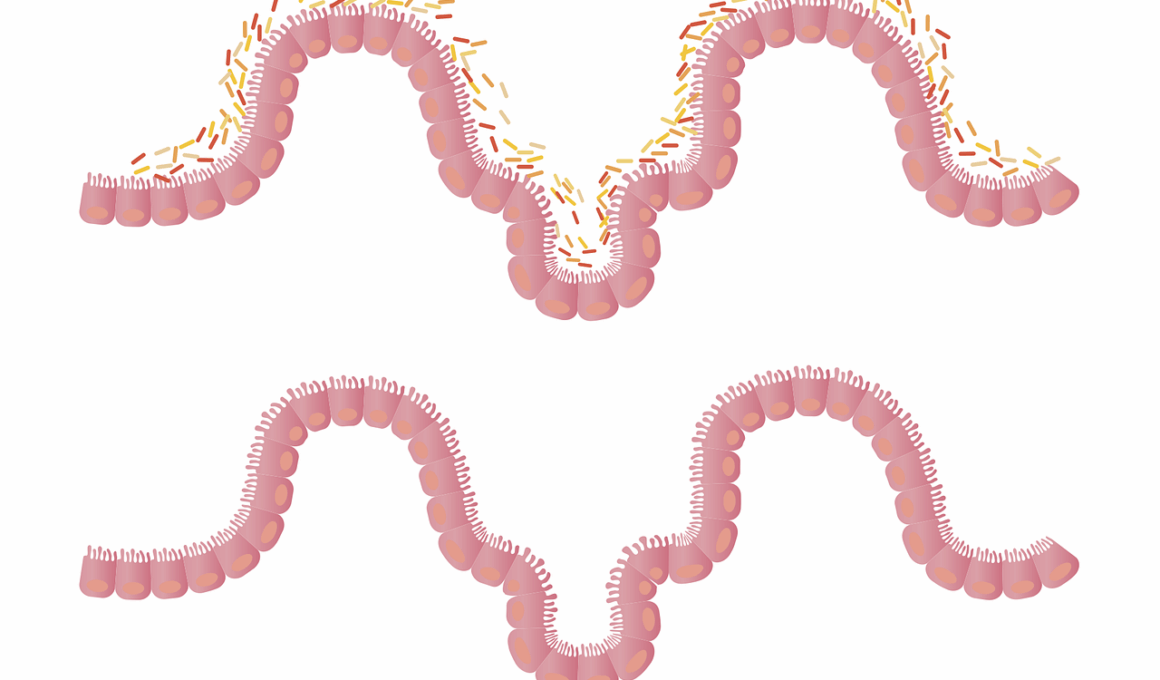
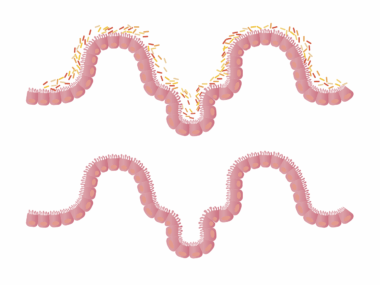
Understanding Gut Dysbiosis
Gut dysbiosis occurs when harmful bacteria outnumber beneficial ones, resulting in various health manifestations. This imbalance can arise from poor dietary choices, chronic stress, antibiotic use, and environmental toxins. Some common symptoms include bloating, fatigue, and hormonal imbalances. One significant area affected by dysbiosis is the endocrine system, which regulates hormonal activity throughout the body. Research indicates that certain gut bacteria play a pivotal role in metabolizing hormones. For example, the bacteria can influence estrogen levels, leading to symptoms of estrogen dominance or deficiency. Furthermore, dysbiosis can also affect thyroid hormone metabolism, resulting in conditions such as hypothyroidism. Studies have shown a connection between specific gut bacteria and cortisol regulation, linking gut health with stress responses. The concept of the gut-brain axis illustrates that gut microbiota can influence hormonal regulation through neurotransmitter production. Addressing gut dysbiosis may involve dietary changes, stress management, and restoring your gut flora. Personalized nutrition plans focusing on whole foods can help maintain a balanced gut microbiome, ultimately promoting hormonal stability and overall health.
Additionally, addressing stress is vital as it negatively impacts gut health and hormones. Chronic stress often leads to gastrointestinal disturbances, and stress hormones can worsen gut dysbiosis. Yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help alleviate stress, promoting a healthier gut environment. Supplements may also play a role in restoring gut flora. Probiotics and prebiotics can help replenish beneficial bacteria and optimize gut function. In particular, probiotics like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains are known for their efficacy in improving gut health. Incorporating fermented foods such as sauerkraut, kimchi, and miso can naturally provide these beneficial bacteria. Furthermore, dietary fiber is essential for feeding gut bacteria, promoting their growth and diversity. Foods rich in soluble fiber, like oats and legumes, should be included in your diet. Adequate hydration is necessary for optimal digestion and can also help maintain a healthy gut lining. Overall, supporting gut health through a comprehensive lifestyle approach can lead to improved hormonal regulation. Monitoring hormone levels periodically can help assess changes resulting from gut health interventions.
The Connection Between Gut Health and Hormones
The interconnectedness of gut health and hormone regulation is increasingly recognized in medical research. Gut bacteria are known to be involved in the synthesis of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that significantly impacts mood and sleep. Any disruption in gut microbiota can lead to decreased serotonin levels and increase the risk of mood disorders. Moreover, gut dysbiosis can influence the gut’s ability to absorb essential nutrients, including vitamins and minerals important for hormone production. Vitamin D, for instance, is crucial for testosterone synthesis, while zinc plays a vital role in regulating cortisol levels. A deficiency in these nutrients due to poor gut health can exacerbate hormonal imbalances. Additionally, chronic inflammation linked with dysbiosis can lead to increased production of cortisol, the body’s primary stress hormone. High cortisol levels can significantly affect various bodily functions, including metabolism and immune response. When cortisol remains elevated, it can result in hormonal disruptions that contribute to weight gain and a host of other health issues. To foster hormonal health, addressing gut health issues should be prioritized, ensuring a balanced intake of nutrients and probiotics for optimal function.
One practical way to enhance gut health is to adopt an anti-inflammatory diet. Such a diet promotes foods rich in antioxidants, healthy fats, and fiber. Examples include colorful vegetables, fruits, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish. These foods support the gut microbiome and mitigate inflammation. Reducing processed foods, added sugars, and trans fats can help restore the balance of gut microbiota. This transition helps protect against oxidative stress, which directly impacts gut health and hormonal function. It may also be beneficial to perform regular detoxification practices. Natural detox methods, such as consuming cruciferous vegetables, support liver function, which plays a vital role in hormone metabolism. Incorporating herbal teas, such as dandelion or green tea, may also support detoxification processes. Furthermore, engaging in regular physical activities and maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for hormonal stability. Exercise can improve gut motility and promote positive changes in gut microbiota composition. This balanced approach incorporates physical health into hormonal management, underlining the relationship between gut health and fitness.
Long-Term Implications of Gut Dysbiosis for Hormonal Health
The long-term implications of untreated gut dysbiosis can significantly affect hormonal health. Chronic hormonal imbalances can lead to various long-term health issues, including diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular diseases. For instance, insulin resistance is a common consequence of hormonal imbalance tied to gut health. Insulin plays a significant role in regulating blood sugar levels; therefore, dysbiosis may lead to metabolic syndrome over time. This syndrome is characterized by a cluster of conditions, increasing the risk of heart disease. Additionally, an imbalance in sex hormones can affect reproductive health. For women, it may lead to issues such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), which is often exacerbated by gut health problems. Men can experience low testosterone levels, affecting energy, mood, and libido. Addressing gut dysbiosis is not merely about immediate symptom relief; it’s essential for long-term hormonal health. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider to monitor hormonal levels can aid in early detection of these issues. Implementing a holistic lifestyle focused on gut health, nutrition, and stress management appears fundamental to sustaining balanced hormones.
In conclusion, the relationship between gut health and hormones is complex yet vital for overall wellness. Recognizing the signs of gut dysbiosis and taking proactive steps can significantly enhance hormonal regulation. Prioritizing a nutrient-dense diet, reducing stress, and promoting physical activity can foster a healthy gut environment. Restoring gut microbiota balance through probiotics and prebiotics should be integral to any health regimen aimed at maintaining hormonal health. Additionally, long-term lifestyle changes can provide considerable health benefits. Engaging with healthcare professionals for personalized guidance can further optimize gut and hormonal health. Combining dietary choices with appropriate supplements and stress-relief practices can create a synergistic effect on overall health. Continuous learning about the gut-hormone connection may enable individuals to make informed decisions regarding their health. Therefore, prioritizing digestion and gut balance is—the cornerstone of achieving and maintaining hormonal health. By committing to improve gut health, we can enhance our quality of life, ensuring that our hormones function optimally and sustain our well-being throughout our lives.