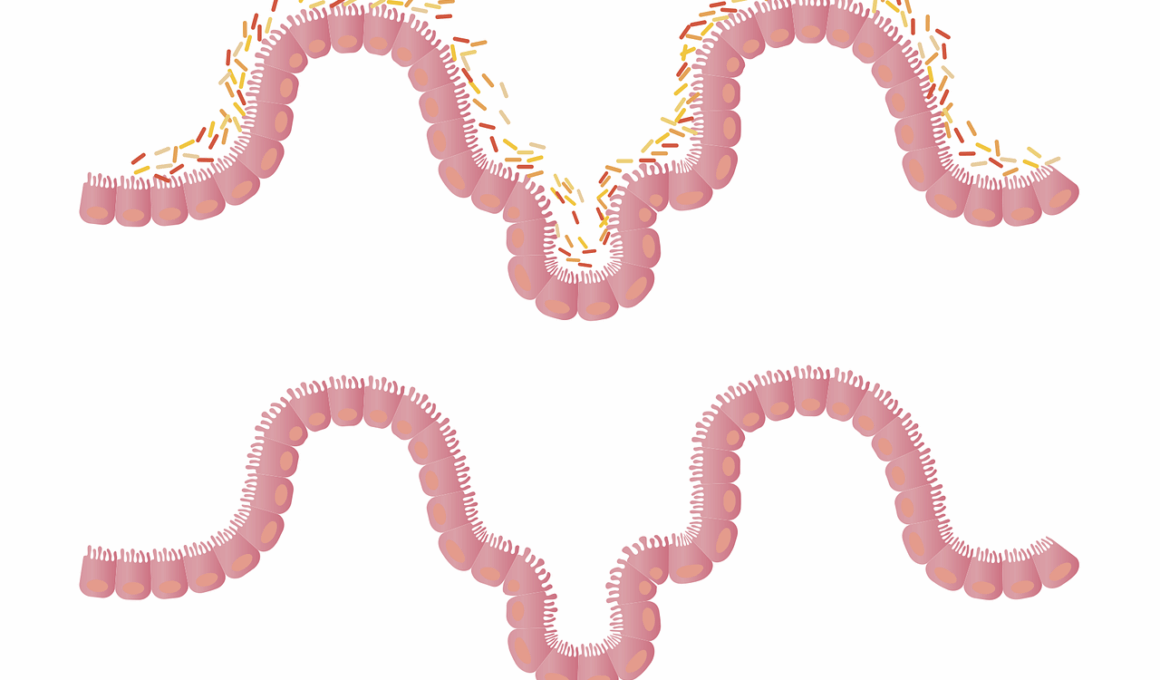
Intermittent Fasting’s Effect on Leaky Gut Syndrome
Intermittent fasting (IF) has gained popularity in recent years, particularly for its potential effects on health, including gut health. The gut microbiome plays a crucial role in digestion and overall well-being. It consists of trillions of microorganisms that interact with each other and the host. Research has shown that fasting influences the composition and diversity of the microbiome in various ways. During fasting, the digestive system gets a break, allowing it to repair and maintain homeostasis. The benefits of intermittent fasting on gut health are notable. Studies suggest that it can reduce inflammation, which is a significant contributor to leaky gut syndrome. This condition occurs when the intestinal barrier becomes permeable, allowing harmful substances to enter the bloodstream. Enhanced gut permeability can result in several health issues, including autoimmune disorders and chronic inflammation. By relying on specific eating windows, IF may help improve gut integrity and reduce symptoms associated with leaky gut. However, individual responses to intermittent fasting can vary widely; as such, it’s important to approach fasting with caution and consider personal health conditions before starting.
One of the primary ways intermittent fasting impacts gut health is through the modulation of gut microbiota. Research has indicated that fasting can positively influence microbial diversity, favoring the growth of beneficial bacteria while suppressing potentially harmful strains. A balanced microbiome is critical for digesting food effectively and maintaining a strong gut barrier. Increased fiber intake during non-fasting periods can further contribute to microbial diversity and health. Foods high in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, promote the proliferation of beneficial bacteria, enhancing gut health. When considering leaky gut syndrome, a healthy microbiome is essential for sustaining the intestinal barrier. Additionally, fasting periods provide the gut with the opportunity to undergo repair and regeneration. Short breaks from food intake allow the gut lining to recover from any wear caused by poor dietary habits. This regenerative process can reduce the symptoms resulting from leaky gut and ultimately improve digestion. Thus, incorporating intermittent fasting may serve as a tool for promoting a balanced microbiome and enhancing gut health, paving the way for better overall wellness.
Fasting and Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is a primary factor contributing to leaky gut syndrome, undermining gastrointestinal health. Intermittent fasting has been shown to possess anti-inflammatory properties that can alleviate this condition. By reducing inflammatory markers in the body, fasting can help restore the integrity of the intestinal lining. This restoration is vital for preventing the passage of toxins and pathogens through the gut wall. The reduction of inflammation is linked to a decrease in the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which further supports gut health. Additionally, fasting can assist in lowering blood sugar and enhancing insulin sensitivity, which can reduce inflammation overall. Research has shown that periods of fasting prompt autophagy, a biological process where cells eliminate damaged components. This cellular cleansing helps maintain gut integrity and overall health. Another benefit of fasting is its role in promoting a healthy weight. Excess body weight is often associated with increased inflammation; therefore, reducing weight through intermittent fasting may provide added benefits for gut health. Overall, intermittent fasting has the potential to significantly impact inflammation levels, leading to better gut health and mitigating the risks associated with leaky gut syndrome.
Furthermore, the timing of food consumption during intermittent fasting plays a critical role in gut health. When individuals consume food in alignment with their body’s natural circadian rhythms, they may experience improved digestion and metabolism. This synchronization can enhance the overall functioning of the digestive system, further safeguarding intestinal health. Studies have shown that irregular eating patterns can disrupt gut microbiota and contribute to various gastrointestinal disorders. By adopting a consistent eating schedule within designated fasting windows, individuals may find improvements in digestive discomfort and overall gut function. Additionally, fasting allows for extended periods of low food intake, giving the gut a chance to rest. This reduction in continuous food processing diminishes the risk of gut dysbiosis, where harmful bacteria outgrow beneficial ones. Moreover, the variety of foods consumed during feeding windows can create an enriched environment for favorable bacteria growth, promoting a stronger gut microbiome. While there is no one-size-fits-all approach, many individuals may benefit from adopting intermittent fasting as a way to regulate their eating patterns and enhance gut health within their unique lifestyles.
The Role of Diet in Intermittent Fasting
While intermittent fasting can greatly affect gut health, it is essential to consider dietary choices made during eating periods. Consuming nutrient-dense foods is crucial for maximizing the benefits of fasting. Foods rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants can support healthy digestion and promote the optimal functioning of the gut. Diets high in processed foods, added sugars, and unhealthy fats can counteract the positive effects of intermittent fasting and may worsen leaky gut symptoms. Instead, incorporating whole foods such as legumes, leafy greens, and fermented products can nurture beneficial gut bacteria. Fermented foods, such as yogurt, kimchi, and sauerkraut, are naturally rich in probiotics, which help maintain a balanced gut microbiome. Prioritizing hydration is also essential during eating windows, as water supports digestion and nutrient absorption. Consuming healthy fats, like avocados and nuts, can provide necessary energy without burdening the digestive system. Combining these dietary strategies with intermittent fasting may enhance the overall effectiveness of gut health improvement, supporting not only intestinal well-being but also offering additional health benefits throughout the body.
As individuals explore intermittent fasting and its effects on gut health, they should be mindful of their specific health needs and preferences. Each person may react differently to fasting based on their unique physiology, health conditions, and lifestyle. It can be beneficial to consult with a healthcare professional before starting an intermittent fasting regimen. This consultation ensures that any underlying health issues are addressed and that fasting aligns with overall health goals. Additionally, tracking and monitoring symptoms can provide insight into how well fasting is improving gut health. Observing any changes related to digestion, energy levels, and overall well-being can help identify the best practices for individual needs. Joining support groups or communities focused on intermittent fasting can also provide encouragement and advice from those with similar experiences. By ensuring that the approach to fasting is tailored to individual circumstances, the potential for achieving optimal gut health can be maximized. It allows individuals to effectively navigate their journey towards improved digestive health through a strategic combination of intermittent fasting and diet.
Conclusion
In conclusion, intermittent fasting presents a promising approach for enhancing gut health and mitigating the effects of leaky gut syndrome. By providing the digestive system with necessary breaks and promoting a balanced microbiome, fasting can restore gut integrity. Additionally, the anti-inflammatory benefits associated with fasting may further contribute to improved gut health and reduced digestive discomfort. The importance of dietary choices during eating windows cannot be understated, as nutrient-rich foods support digestion and overall well-being. Personalized approaches to intermittent fasting that respect individual health considerations can offer the best results. While further research is required to fully understand the intricacies of fasting and gut health, existing evidence highlights its potential advantages. Successfully implementing intermittent fasting, along with mindful dietary choices, can lead to a healthier gut and improved quality of life. Embracing this approach with awareness and guidance can unlock the many benefits it has to offer, transforming not only gut health but general wellness in the long run.
In summary, intermittent fasting holds promise as an effective strategy for promoting gut health and addressing leaky gut syndrome. As this wellness trend continues to evolve, it offers hope for individuals seeking improvements in digestive function and overall health through educated dietary and fasting practices.