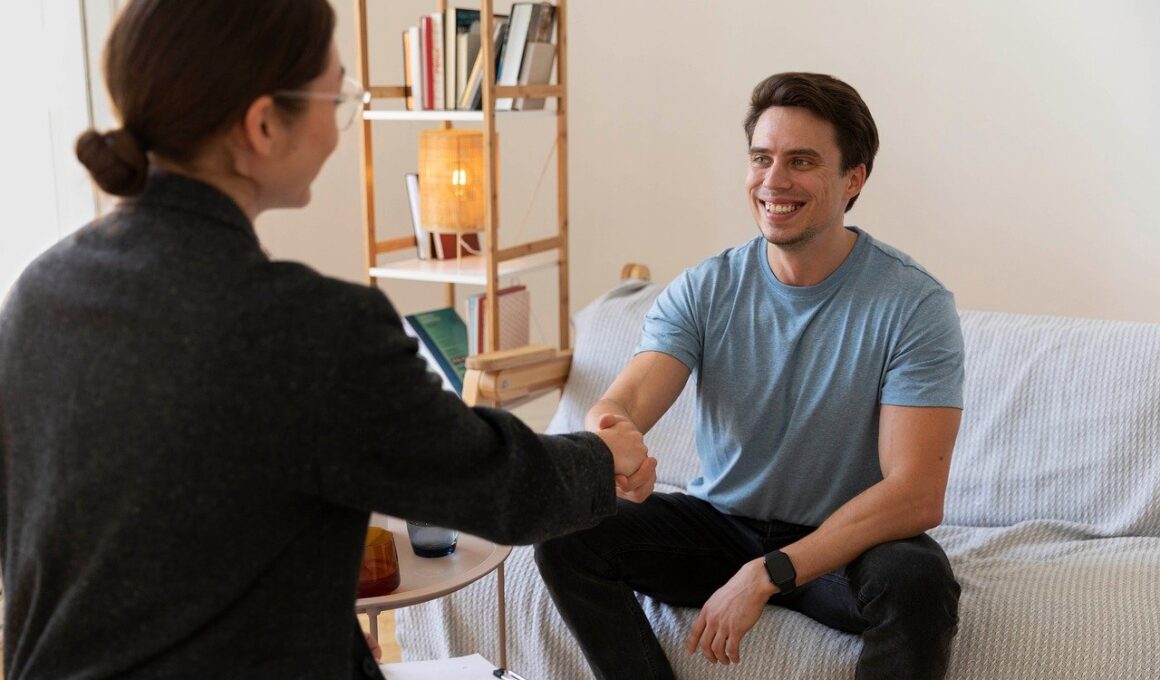
Cultural Perspectives on Trauma and Resilience
Trauma profoundly impacts mental health and well-being, reflecting diverse experiences shaped by cultural context. Different cultures interpret trauma uniquely, leading to varied coping mechanisms and resilience strategies. Understanding these cultural perspectives allows mental health professionals to provide more effective, individualized care. For instance, some cultures may view trauma through a spiritual lens, integrating traditional healing practices into recovery. These cultural interpretations not only influence how trauma is processed but also dictate the available support systems. Community-based support, often more prevalent in collectivist cultures, serves as a buffer against the effects of trauma. Compared to individualistic cultures promoting self-reliance, community ties can offer vital emotional sustenance. Resilience in many cultures arises from communal narratives, fostering strength through shared experiences. This collective resilience helps individuals navigate their trauma while drawing support from social networks. Moreover, cultural rituals may serve as significant healing mechanisms, providing individuals with a sense of belonging and identity. By acknowledging these cultural narratives and practices, mental health interventions can be tailored to resonate with clients, ultimately improving treatment outcomes and fostering a deeper understanding of trauma’s impact across different populations.
Exploring cultural narratives around trauma can enhance our understanding of resilience. Within various cultural frameworks, stories and experiences shared by community members serve as powerful tools for healing. Indigenous cultures, for example, often utilize oral traditions to transmit lessons learned from collective suffering. These narratives not only validate individual experiences but also offer coping strategies rooted in cultural history. Narratives of resilience may emphasize harmony with nature, spiritual healing, and communal support, fostering a holistic approach to recovery. Furthermore, culturally specific resilience strategies, such as community ceremonies, help individuals reconnect with their identity and heritage. These strategies encourage the acknowledgment of trauma within a broader context, allowing for healing not just on an individual level but collectively. Understanding these narratives enables practitioners to design culturally sensitive interventions that integrate these valuable insights. In many instances, such culturally informed practices lead to improved engagement and efficacy in therapeutic settings. Moreover, respecting cultural narratives fosters trust between clients and professionals, ultimately enhancing the therapeutic alliance. By incorporating these elements, mental health services can address trauma in ways that honor individual and community experiences, promoting sustainable resilience grounded in each culture’s unique historical and social contexts.
Impact of Culture on Trauma Interpretation
The interpretation of trauma is profoundly influenced by cultural contexts. Each culture carries its beliefs, values, and narratives that shape how individuals perceive and respond to traumatic experiences. For example, in some cultures, trauma may be viewed as a test of faith, while others may see it as an injustice requiring systemic change. These differing perspectives impact the type and intensity of emotional responses individuals exhibit, and consequently, their healing process. Language also plays a crucial role in how trauma is expressed and understood. Certain cultures may have specific terms or concepts that encapsulate trauma, providing a framework for individuals to articulate their experiences. Additionally, societal attitudes toward mental health can either stigmatize or normalize discussions around trauma, influencing willingness to seek help. For instance, cultures that prioritize mental wellness may incorporate trauma-informed care directly into their healthcare systems, increasing accessibility. In contrast, cultures that stigmatize mental health may obstruct recovery paths. Understanding these varying interpretations enhances the ability of mental health professionals to tailor interventions that align with cultural beliefs, ultimately bridging the gap between clinical practice and cultural sensitivity in addressing trauma.
Cultural stigma surrounding mental health often presents barriers to treatment, affecting individuals’ willingness to seek help. In many communities, mental health issues, including the effects of trauma, are shrouded in shame and misunderstanding. These stigmas can prevent open conversations about trauma, leading to isolation and further exacerbation of mental health struggles. Additionally, cultural beliefs about masculinity or strength can deter people from acknowledging vulnerability as a natural response to trauma. For example, in some cultures, expressing emotions or seeking external help may be perceived as weakness, reinforcing damaging norms. The negative consequences of such stigma can be profound, as it diminishes the chances of receiving necessary support, both from professionals and within one’s own community. Mental health education campaigns aimed at deconstructing these stigmas are vital. By encouraging open discussions around trauma and mental health, fewer individuals will hesitate to reach out for help. Furthermore, culturally-appropriate resources can empower communities to address these issues, fostering environments that promote mental well-being. Mental health professionals must prioritize tackling stigma to create inclusive spaces where individuals feel safe to seek support, ultimately fostering resilience within culturally diverse populations.
Coping Mechanisms Across Cultures
Coping mechanisms employed by individuals in various cultures reflect the unique ways societies respond to trauma. These mechanisms can range from individualistic strategies, such as journaling and self-reflection, to collectivist approaches emphasizing community and family support. In some cultures, coping strategies may involve rituals, such as prayer or meditation, which serve to connect individuals to their cultural heritage and promote emotional healing. These practices enhance overall well-being while providing frameworks for understanding personal experiences of trauma. Moreover, traditional healing practices, such as herbal medicine or spiritual counseling, are often integral components of coping in many cultures. These strategies reinforce a sense of belonging and identity. Understanding and incorporating these cultural coping mechanisms into mental health interventions can significantly enhance treatment effectiveness. Culturally competent care better aligns therapeutic practices with clients’ values, thus fostering a collaborative environment where individuals feel understood and supported. By facilitating access to culturally relevant resources, mental health clinicians can empower clients to leverage their inherent resilience and develop effective coping strategies. This approach emphasizes the importance of viewing trauma and recovery through a culturally sensitive lens that recognizes the richness of diverse healing traditions.
Resilience is often framed within the context of culture, and this perspective highlights the interplay between individual experiences and community narratives. Understanding how different cultural groups define and cultivate resilience provides insight into effective mental health support strategies. For example, in some Eastern cultures, resilience may be rooted in family interconnectedness, emphasizing mutual support as key to overcoming adversity. Conversely, Western cultures often stress personal strength and independence as critical components of resilience. While these definitions differ, they underscore the importance of context in shaping individuals’ responses to trauma. Engaging with cultural definitions of resilience can enhance the mental health care experience for clients. This includes fostering an understanding of how cultural backgrounds influence coping strategies, support systems, and healing narratives. Mental health professionals may facilitate resilience-focused discussions to create tailored interventions that resonate with their clients’ cultural experiences. Recognizing and integrating clients’ perspectives on resilience into therapeutic settings cultivate a sense of empowerment and validation. Furthermore, acknowledgment of cultural strengths fosters a collaborative therapeutic environment where individuals feel recognized and supported in their journey toward healing and recovery following traumatic experiences.
Conclusion: The Way Forward
Moving forward, the field of mental health must prioritize cultural sensitivity when addressing trauma and resilience. As societies become increasingly diverse, understanding the multifaceted nature of trauma across cultural contexts becomes paramount. This involves recognizing and valuing different coping mechanisms, resilience narratives, and cultural attitudes towards mental health. Comprehensive training for mental health professionals in cultural competence is essential to achieve effective support for individuals from various backgrounds. Integrating cultural perspectives into assessment and treatment practices will enhance therapeutic outcomes. Furthermore, fostering community-based initiatives that promote mental health education will help reduce stigma, encouraging open discussions surrounding trauma. Establishing networks that connect individuals to culturally relevant resources empowers communities. Initiatives such as workshops or support groups can bridge gaps between traditional healing practices and modern clinical approaches to mental health. Collaborative efforts between mental health professionals and community leaders can further foster environments conducive to healing and resilience. By advocating for culturally informed practices, we create pathways for individuals to confront trauma while nurturing their unique strengths and identities. This allows for a transformative journey toward healing, ensuring that all voices are heard and valued in the mental health conversation.
In conclusion, embracing cultural perspectives on trauma and resilience is critical in the realm of mental health. As we navigate an ever-evolving understanding of mental well-being, it is essential to appreciate the diversity of experiences shaped by cultural backgrounds. By honoring these perspectives, practitioners can enhance their sensitivity to the nuances of trauma and resilience, creating a more inclusive environment for healing. This purposeful integration of cultural understanding into mental health practices promotes improved engagement, empathy, and effectiveness in treatment outcomes. Recognizing the significance of cultural narratives can ultimately empower individuals to express their experiences, seek help, and cultivate resilience. As discussions and research surrounding mental health continue to progress, the importance of cultural competence in practice cannot be overstated. In fostering a culturally inclusive approach, we not only acknowledge the diverse experiences of trauma but also enhance the potential for holistic recovery through nurturing individual and communal strengths. Thus, promoting a collective commitment to mental health awareness grounded in cultural respect is essential for shaping a brighter and more resilient future for all.