Sustainable Protein Sources: Beyond Meat and Dairy
In recent years, the awareness surrounding sustainable eating practices has significantly increased, leading to a shift in consumer preferences. People are beginning to recognize the environmental impact of traditional meat and dairy production. Consequently, many are searching for alternatives that offer sustainable protein sources. Plant-based proteins like lentils, chickpeas, and quinoa are not only rich in essential nutrients but also have a considerably lower carbon footprint compared to animal products. These alternatives cater to various dietary needs, ensuring that everyone can benefit from them. Moreover, diversifying protein sources can enhance overall dietary quality by incorporating a wider array of vitamins and minerals. Foods such as hemp seeds, nuts, and seeds provide additional healthy fats and proteins that support a balanced diet. Fungus-derived proteins, like mycoprotein found in products such as Quorn, are also gaining recognition as an innovative meat substitute. Furthermore, switching to sustainable protein sources can contribute to improved health outcomes and reduced greenhouse gas emissions. By exploring various plant-based options, individuals can actively participate in promoting a more sustainable future while nourishing their bodies with high-quality protein.
Exploring Plant-Based Options
Legumes, including beans and peas, are also excellent sources of protein. They are versatile, affordable, and exceptionally nutritious. Incorporating legumes into meals can lead to mindful consumption, thereby promoting sustainable eating overlooked for years. In addition to enhancing dietary protein, legumes contribute to environmental well-being by improving soil health. They are nitrogen-fixing plants, meaning they enhance soil fertility, which can improve cropping systems and biodiversity. Sustainable eating practices encourage consumers to focus on whole foods that minimize processing. Products like tempeh and tofu made from soybeans are increasingly gaining popularity, as they provide substantial amounts of protein while remaining environmentally friendly. Moreover, innovations in plant-based technologies are making it easier for brands to create products mimicking the texture of meat, which can help in the transition for those resistant to switching. It is vital to consider where ingredients are sourced since the local availability of plants can reduce the environmental impact associated with transportation. This practice not only supports local economies but also promotes a greater appreciation for seasonal eating that aligns with sustainable food practices.
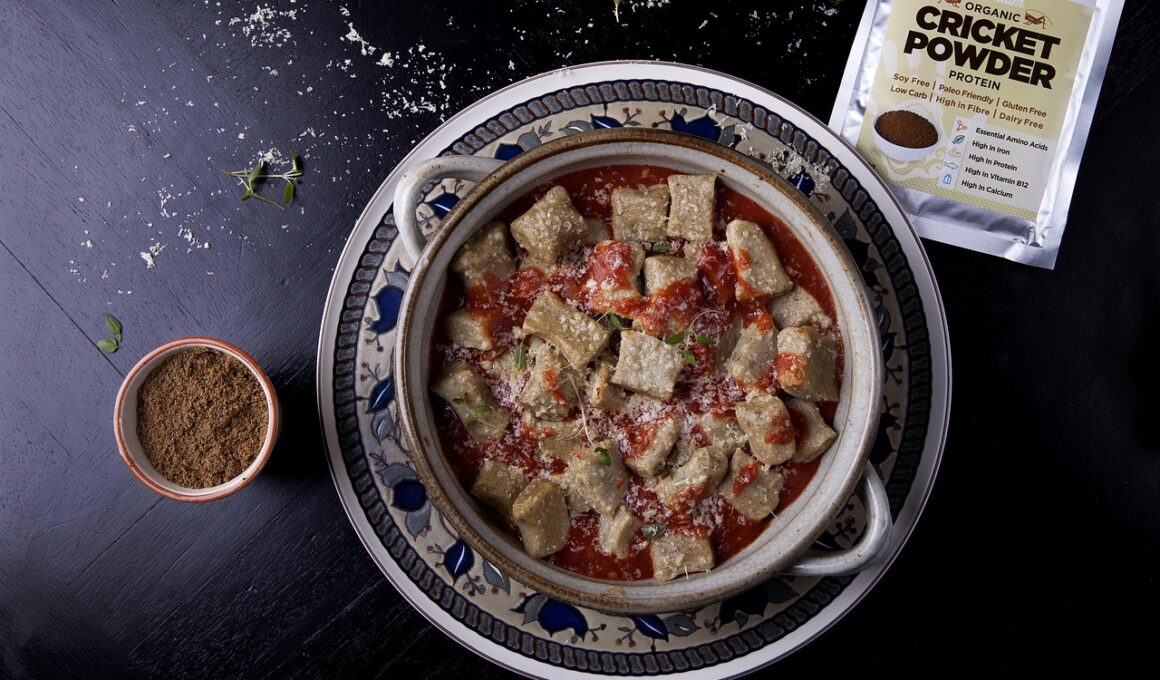
Another intriguing option emerging in sustainable protein sources is insect consumption. Though it may seem unconventional in Western cultures, many countries have been consuming insects for centuries. Crickets, mealworms, and grasshoppers are rich in protein, containing equal or even higher protein levels compared to conventional meat. Additionally, raising insects generates significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions and requires much less land and water than traditional livestock farming. As awareness elevates, food cultures are adapting to include insect proteins in various recipes, allowing a novel approach to sustainability. Companies are working towards developing protein powders and snacks made from insect protein, aiming to break the stigma attached to entomophagy. Participation in this dietary trend can contribute to a more balanced ecosystem and tackle the protein gap as the population grows. Entrepreneurs are forging paths in creating appetizing insect-based products in areas like energy bars and protein shakes. Engaging with insect protein presents not only an eco-friendly alternative but also an opportunity for culinary innovation and exploration. Multi-faceted, objective dialogue on this subject is essential for reshaping societal perceptions toward sustainable eating.
Health Implications of Sustainable Eating
Beyond environmental concerns, it is important to consider the health implications tied to adopting sustainable eating habits. By incorporating more plant-based proteins, people can benefit from lower cholesterol levels, reduced risks of heart disease, and better weight management. Additionally, these diets tend to be rich in dietary fiber, crucial for healthy digestion and maintaining energy levels. A focus on diverse food groups ensures that individuals receive the right balance of vitamins and minerals needed for overall well-being. Balancing nutrient-dense foods with sustainable practices can lead to a healthier lifestyle without compromising the environment. Furthermore, many plant-based foods offer antioxidants that help combat oxidative stress and inflammation in the body. As consumers become more health-conscious, they are likely to seek products that not only taste good but also bring essential health benefits. Therefore, it is critical for people to become educated on the nutritional values of various protein sources and how they fit into a sustainable diet. Exploring the synergy between health and sustainability fosters a more holistic approach to dietary decisions that extends beyond just individual choices.
Environmental awareness has sparked a growing interest in local and sustainable food systems, significantly reducing the reliance on heavily processed and non-renewable resources. Community-supported agriculture (CSA) initiatives and farmer’s markets are increasing, allowing direct access to local produce and sustainable protein sources. By engaging with local agriculture, consumers contribute towards revitalizing local economies while promoting fresh, seasonal produce consumption. This relationship supports sustainable farming practices that prioritize soil health and responsible animal husbandry, inherently reducing the carbon footprint associated with food production. Moreover, education around local sourcing encourages community engagement, fostering conversations about health and environmental practices. Individuals can explore their town’s offerings, abandoning corporate chains in favor of locally-grown options. This shift also allows for greater transparency in food systems, providing clarity on the origin of products consumed. Additionally, it enhances food security and resilience by reducing dependence on a vulnerable global food network. Choosing to support local farmers can cultivate communal bonds and diversify available proteins, enabling families to make more sustainable food choices that benefit their health and the environment alike.
The Role of Education in Sustainable Nutritional Practices
Education plays a crucial role in promoting sustainable eating practices by equipping individuals with knowledge about nutrition and environmental impact. When consumers understand the implications of their food choices, they are more likely to opt for sustainable protein sources. Schools, communities, and organizations can implement programs that raise awareness of the benefits associated with a plant-based diet. Furthermore, education around cooking techniques encourages families to experiment with diverse ingredients and develop cooking skills for healthier meal options. Workshops and online tutorials can provide accessible knowledge about integrating sustainable foods into daily lives, empowering people to adopt these practices advocate for responsible consumption. Understanding food labels and the significance of sourcing allows consumers to make informed choices while shopping. Local organizations can facilitate workshops, cooking classes, and interactive events that focus on sustainable nutrition, helping participants discover exciting new foods and recipes. In this way, education fosters a culture of sustainability whereby individuals acknowledge the larger societal impacts of their consumption choices. By learning how to make sustainable practices feasible at home, significant environmental changes can be achieved through collective efforts.
Supporting sustainable food movements not only enhances overall health but also galvanizes deeper societal shifts towards a better future. Collaboration between consumers, producers, and policymakers is essential for developing impactful solutions to food-related challenges. By advocating for plant-based protein sources and supporting local systems, individuals can contribute to a more sustainable food chain. Encouraging conversation around sustainable practices in community events will further raise awareness and enthusiasm towards responsible consumption. This, in turn, may inspire brands to prioritize eco-friendly practices and create more products that align with the values of conscious consumers. Establishing policies that support sustainable agriculture and responsible food production will embolden current and future leaders to champion sustainability initiatives while tightening the connection between nutrition and environmental health. Emphasizing the importance of sustainability through practical examples will help people demand better from themselves and their leaders. Ultimately, this collective effort contributes to transforming dietary habits towards reduced environmental impact and improved health outcomes. As consumers increasingly prioritize their values in their purchasing decisions, the idea of sustainable eating practices will undoubtedly become more mainstream.