HIIT Myths and Facts Related to Heart Health
High-Intensity Interval Training, commonly known as HIIT, has gained immense popularity in recent years due to its effectiveness in enhancing overall cardiovascular health. Many enthusiasts quickly adopt this method, believing it represents a shortcut to fitness. However, it’s essential to understand both the advantages and misunderstandings prevalent around HIIT practices. One myth is that HIIT is exclusively for elite athletes or those in exceptional shape. In reality, individuals of all fitness levels can incorporate HIIT into their routines with appropriate modifications. Moreover, another misconception is that HIIT can replace traditional aerobic exercises entirely. While HIIT offers many benefits, steady-state cardio is still vital for heart health and endurance. It’s beneficial to alternate between different training styles to attain balanced fitness. According to research, engaging in moderate to high-intensity exercise like HIIT can improve heart health, lowering blood pressure, enhancing circulation, and reducing cardiovascular disease risk. Overall, ensuring safety and adapting any exercise routine to fit personal health is crucial for maximizing the benefits of HIIT without compromising safety and wellness.
Understanding HIIT and Its Impact on Cardiovascular Health
The essence of HIIT lies in short bursts of intensive activity alternated with rest or lower-intensity intervals. This method promotes increased heart rate, stimulating the cardiovascular system significantly. Studies indicate that such training can improve heart efficiency and overall endurance when performed correctly. Engaging in HIIT not only burns calories rapidly but also enhances metabolic flexibility. This dual-action makes it a compelling option for those looking to improve fitness in limited daily timeframes. While many people cherish these rapid results, they often overlook the importance of recovery. Recovery plays a crucial role in maximizing gains and avoiding burnout or injury. For individuals aiming to improve cardiovascular health, integrating HIIT with adequate recovery and balanced nutrition is essential. Misguided beliefs may lead to the assumption that everyone should perform HIIT daily; however, most experts recommend doing it two to three times weekly. Pairing HIIT with strength training or flexibility work can create a comprehensive routine. It’s vital to listen to your body and adjust the intensity based on individual experience and condition to optimize heart health benefits from HIIT without adverse effects.
Common concerns arise regarding the safety of HIIT, particularly for older adults or those with pre-existing health conditions. Engaging in such intense workouts may seem intimidating and unrealistic to many. However, research shows that even individuals with cardiovascular issues can participate in HIIT, given they follow several precautions. Consulting a healthcare professional prior to starting any new fitness regime is always advisable. They can recommend tailored modifications based on individual fitness levels and health status. Furthermore, proper warm-up and cool-down sessions before and after exercising can significantly mitigate risks associated with high-stress workouts. Incorporating a variety of exercises part of HIIT can help avoid stress concentrations on any specific body parts. Thus, adapting HIIT to fit personal abilities enhances the experience while minimizing risks associated with faster workout sequences. Additionally, one should remain attentive to any symptoms that may indicate overexertion or injury. Cardiac anomalies should take precedence, and monitoring heart rate during exercises is an excellent practice for HIIT participants. Ultimately, with informed planning, HIIT can be a safe and beneficial exercise method for heart health across diverse demographics.
Debunking Common Misunderstandings About HIIT
One prevalent misconception about HIIT is that it is a new concept, but history reflects different high-intensity training methods long before the current name emerged. Various athletes have employed similar tactics while training for decades. The periodization model often incorporated high-intensity phases highlighted through interval training principles. Therefore, while HIIT might be trendy in modern fitness parlance, aspects of the training style have origins rooted in athletic training traditions. Moreover, there’s a pervasive belief that longer workouts yield better results. Research demonstrates that shorter and more intense workouts can lead to remarkable improvements in cardiovascular fitness compared to longer sessions at lower intensities. HIIT, lasting only 15 to 30 minutes, can promote impressive aerobic and anaerobic gains when executed appropriately. Many perceive that weight loss is the only significant factor driven by HIIT; combating this notion expands understanding of health benefits. HIIT also boosts hormonal responses, leading to increased muscle retention during fat loss. Emphasizing correct techniques and safety measures is vital for those engaging in HIIT, ultimately shaping a robust understanding and experience with high-intensity training.
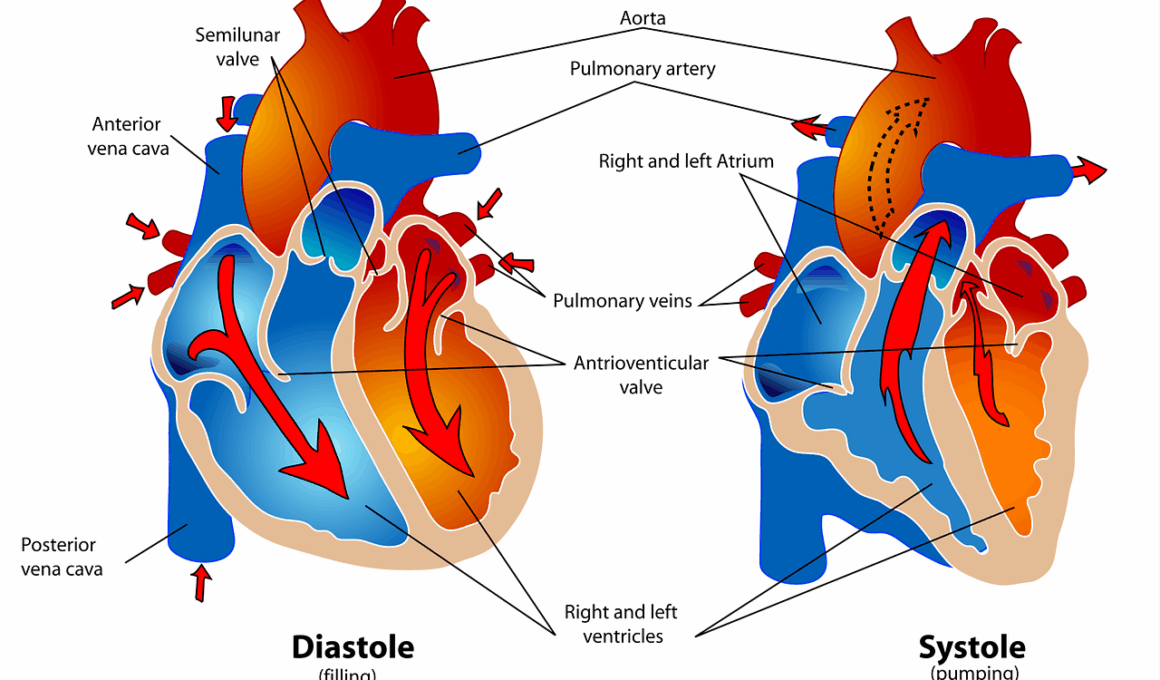
The connection between HIIT and heart health is deeply rooted in metabolic sciences. HIIT engages both aerobic and anaerobic pathways by alternating between high-energy expenditure and recovery. Such anaerobic intervals lead to greater oxygen consumption, ultimately enhancing cardiovascular efficiency. The heart, in response to challenges posed by high-intensity intervals, becomes stronger and more resilient to stress. Consequently, research suggests that incorporating HIIT into regular fitness routines can lead to lower resting heart rates and improved blood lipid profiles. Nevertheless, while cardiovascular benefits multiply, attention to form and technique is essential to optimize results. Adopting incorrect techniques during HIIT can increase the likelihood of injury and negate potential health benefits. Thus, practicing with knowledgeable instructors can help those new to HIIT refine their approach. Additionally, combining HIIT with heart-healthy practices, including balanced diets and regular check-ups, creates a holistic approach to overall wellness. Understanding individual limits and gradually acclimating to new intensity levels cultivates safer and more effective engagements with this type of training. Having a balanced approach fosters not only improved cardiovascular health but holistic well-being, maximizing the advantages of HIIT training methods.
The Importance of Tailoring HIIT for Individual Needs
Every individual’s body responds differently to exercise, and understanding personal thresholds is pivotal when navigating HIIT practices. Factors such as age, previous injury history, and overall fitness levels affect how one should approach HIIT programming. Consequently, creating personalized HIIT routines can ensure successful outcomes while protecting personal limits against injury or overtraining. Many experts advocate for beginning with lower-intensity intervals before progressively increasing intensity based on comfort levels. Additionally, focusing on proper recovery is equally vital. Failure to allocate time for recuperating interferes with performance improvements and may lead to physical setbacks. Integrating flexibility and strength training alongside HIIT can offer supplementary benefits by providing necessary muscle conditioning while improving functional capabilities. Moreover, individuals recovering from cardiovascular events must take extra precautions while learning correct methods. Specialized programs may exist targeting clients recovering from various medical conditions, blending medical oversight with exercise. This tailored approach to HIIT accommodates various abilities and aspirations, ensuring that everyone has the opportunity to leverage its benefits safely. Individualized HIIT programs create pathways for many to engage with high-intensity exercise while promoting long-term cardiovascular health.
In conclusion, HIIT is a method that holds immense promise for enhancing cardiovascular health for various individuals, regardless of current fitness levels. However, it is surrounded by myths and potential misunderstandings that could lead to improper engagements. Seeking guidance from professionals and tailoring exercise routines are pivotal in harnessing its benefits. Additionally, keeping track of body responses to intensities and allowing adequate recovery lead to safer and more fruitful experiences with HIIT. Balancing various exercise styles while ensuring proper technique reinforces cardiovascular health efforts, confirming that high-intensity practices do not exist in isolation but rather within overall fitness regimens. Emphasizing the importance of individual capabilities cultivates better relationships with fitness and continuous improvement. Thus, encouraging the integration of regular HIIT into lifestyles can lead to lasting changes in how individuals approach health and fitness. By debunking myths surrounding HIIT and establishing a solid understanding, more people can confidently include these workouts in their routines, helping them achieve optimal cardiovascular health goals. HIIT not only enhances physical outcomes but can nurture mental resilience and self-confidence as individuals witness the improvement in their performance and overall wellness.