Protein Intake Strategies for Endurance vs. Strength Training
Post-workout nutrition is essential for recovery and performance improvement. For endurance athletes, the focus post-exercise is on replenishing glycogen stores and facilitating recovery. This begins with consuming high-quality protein sources, such as chicken, fish, or plant-based protein options like legumes or tofu, which support muscle repair. Adding carbohydrates, such as whole grains or fruits, helps restore energy levels depleted during long-duration activities. It is pivotal that endurance athletes consume approximately 1.2 to 1.4 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight to aid recovery effectively. To optimize recovery, consider timing your protein intake around the workout window. Consuming a protein-rich snack or meal within 30 minutes post-exercise can amplify muscle protein synthesis and recovery. Shake supplements, bars, or smoothies are effective strategies for ensuring adequate protein intake when schedules are tight. Ultimately, personal preferences and dietary restrictions must be acknowledged to customize protein sources. Tailoring protein intake strategies to match endurance training can accelerate recovery and enhance overall performance.
Strength training, in contrast, emphasizes muscle hypertrophy, which necessitates a different protein strategy post-workout. The goal here is to promote muscle growth and repair after intense resistance sessions. Strength athletes should target a protein intake of approximately 1.6 to 2.2 grams per kilogram of body weight to maximize gains. Fast-digesting proteins, such as whey protein shakes or lean poultry, can effectively stimulate muscle protein synthesis when consumed shortly after workouts. It is essential to consume protein in conjunction with carbohydrates to replenish glycogen stores for optimizing recovery and supporting future workouts. Consider incorporating sources such as brown rice, oats, and sweet potatoes alongside protein. Timing remains crucial; aim to consume protein within a one to two-hour window following the workout for optimal muscle recovery and growth. Additionally, integrating a variety of protein sources throughout the day can aid in meeting the overall protein requirement. Experiment with different combinations of protein-rich foods, shakes, or bars to find what aligns with personal preferences, enhancing post-workout nutrition strategies.
Timing Matters: Endurance vs Strength
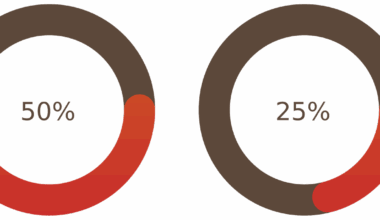
The timing of protein intake is critical for both endurance and strength training. For endurance athletes, recent studies indicate that consuming protein immediately after a workout can lead to greater glycogen replenishment. Combining protein with carbohydrates has been shown to optimize recovery processes. A 3:1 ratio of carbohydrates to protein post-exercise is often recommended for endurance athletes, which significantly accelerates recovery. On the other hand, strength trainers can take advantage of a slightly broader window for protein intake. Consuming protein within two hours post-workout is effective in stimulating muscle growth and repair. This flexibility allows strength athletes to focus on overall daily protein intake rather than strict timing. However, incorporating a quick protein source immediately post-exercise can enhance recovery after challenging sessions. For both types of training, utilizing a mix of whole foods and easily consumable protein sources provides variety and sustenance post-workout. Tailoring the timing of protein intake to specific training regimens can strategically boost performance outcomes and recovery rates.
Protein sources vary widely, and selecting the appropriate options can significantly impact recovery. For endurance athletes, it is vital to choose high-quality, easily digestible protein. Some examples include cottage cheese, yogurt, nut butter, and smoothies containing whey or plant-based powder. These sources not only supply protein but can also be easily combined with carbohydrates. Strength training-oriented athletes should lean towards protein sources with higher leucine content, a branched-chain amino acid crucial for muscle synthesis. Chicken breast, beef, and fish are excellent choices here. Furthermore, for those with vegan or vegetarian diets, beans, lentils, and quinoa provide essential amino acids necessary for recovery. It’s also essential to keep hydration in mind; fluids remain a crucial part of post-workout recovery, so remember to drink adequate water when consuming meals or snacks high in protein. The blend of macro and micronutrients plays a role in recovery optimization. Thus, diversifying protein intake can lead to enhanced muscle recovery and performance, making it worthwhile to experiment with various protein sources.
Impact of Protein Timing on Recovery
The impact of protein timing on overall recovery cannot be overstated. For endurance athletes, prioritizing post-workout protein and carbohydrate intake can improve glycogen resynthesis rates, enhancing subsequent performance. This rapid replenishment is essential for those undertaking repeated endurance sessions. Strength training athletes, likewise, benefit from structuring their protein timings with their workout schedule. The repair and rebuilding of muscle fibers are optimized by the timely intake of protein and carbohydrates. Consuming food during the anabolic window enhances recovery, mitigates muscle soreness, and prepares the body for future sessions. Research consistently supports the notion that the two-hour post-workout window is crucial for strength training recovery. Nevertheless, protein consumption should also be strategically placed throughout the day to ensure that muscle protein synthesis is stimulated frequently. By achieving a higher total daily protein intake, athletes of all types can benefit from improved muscular adaptations. Continuous adjustments based on workout intensity and energy levels are essential to maximizing recovery through precise post-workout nutrition.
Supplements often come into play for both endurance and strength athletes looking to ensure adequate protein intake post-workout. Protein powders, particularly whey, casein, or plant-based proteins, can serve as convenient options for quick recovery. These supplements are easily absorbed and can be tailored to meet specific macronutrient needs. Many athletes find protein bars a practical way to incorporate protein quickly into their diets, particularly when on-the-go. However, whole food sources should still make up the majority of protein intake due to their additional nutritional benefits. Including options such as eggs, lean meats, and legumes ensures that the body receives vital micronutrients. Keeping protein intake varied with supplements should align with an athlete’s specific goals, ensuring they either prioritize muscle recovery or general endurance. Additionally, considering the quality of ingredients in protein supplements is necessary to avoid unwanted additives. Ensure the chosen product meets personal dietary preferences while providing sufficient protein. Contextualize supplementation as a tool among an overall nutritious diet aimed at fueling performance.
Conclusion: Tailor Your Protein Approach
In conclusion, tailoring protein intake strategies specifically to your training focus is vital for optimal recovery. Endurance and strength athletes have distinct needs linked to their workouts. Prioritizing protein types, timing, and sources respectively can enhance performance outcomes and personal health. For endurance athletes, balancing high-quality protein with carbohydrates post-exercise maximizes glycogen replenishment. In contrast, strength training calls for a higher protein intake focused on muscle synthesis and recovery. Daily total protein intake is pivotal for both, enabling effective muscle repair and growth. It is advisable to adopt a flexible approach and be open to experimenting with various protein sources and timings. This adaptability can lead to improvements in overall dietary satisfaction during the post-workout recovery phase. Regular evaluations of your nutrition plan should be conducted to adjust as needed, depending on workout intensity, goals, and recovery speed. By tailoring approaches to fit personal preferences and training regimens, you can achieve significant results in overall athletic performance while enhancing muscle recovery capabilities.